by Bryant Eastham | Apr 9, 2015 | C, DOF, Programming, Technical
Today Panasonic contributed an implementation of the OpenDOF protocols in C. This implementation is fully compatible with the previously released Java libraries, and allows interconnected systems that use any mixture of the two libraries. Panasonic will continue to contribute code over the next months.
by Bryant Eastham | Mar 30, 2015 | News, OpenDOF Project
Our first week had some amazing news coverage!

by User | Mar 25, 2015 | Programming, Technical
Good news, the source code is available here!

by User | Mar 25, 2015 | News
It’s been a busy week!
Thank you to everyone for their help, questions and participation.
by User | Mar 23, 2015 | Downloads, Help, Information, Training
Launching the DOF Console
Extract the DOF Console.zip file, in its entirety, to a location of your choice.
Note: Since there is no installer for the DOF Console, the program launches directly from the folder created during its extraction.
Open the folder created during the extraction.
Double-click the file DOF Console.exe to launch the DOF Console.
by Jon Stringer | Mar 18, 2015 | Basics, Downloads, Help, Programming, Technical, Training
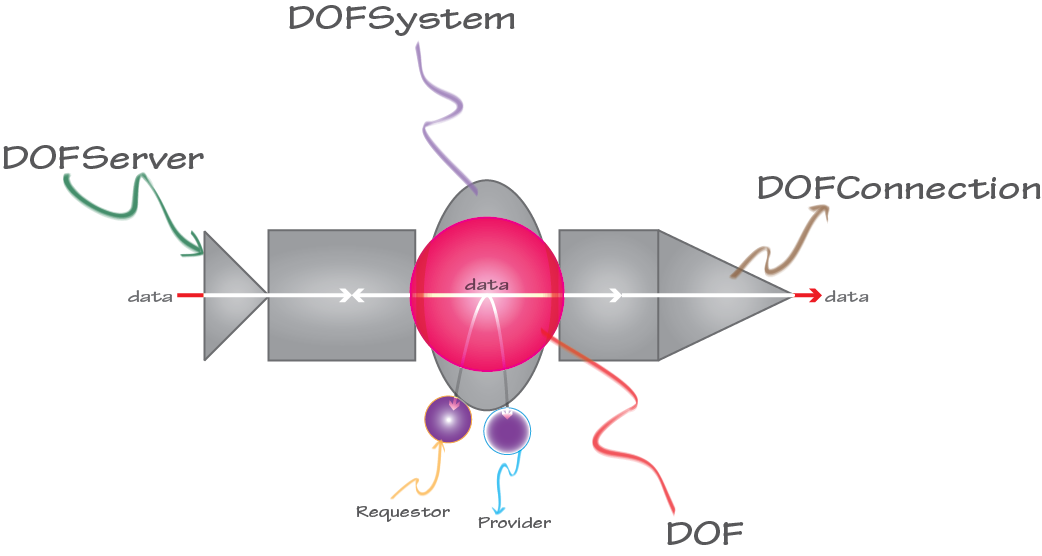
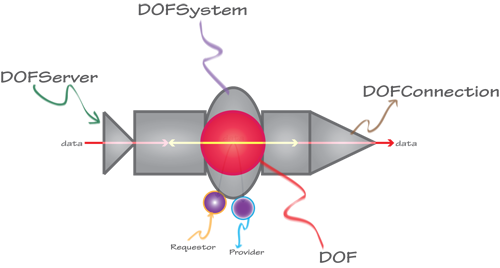
“DOF” is an acronym that defines the underlying technology supported by the OpenDOF Project. “Distributed” refers to the way objects and aspects of an object are distributed on a network. “Object” refers to the DOF Object Model, which ensures greater security and flexibility. And “Framework” refers to the fact that this is a complete solution that can be integrated into your application. To put it another way, DOF technology allows many different products, using many different standards, to more easily share information across many different networks. So whether you are networking a simple or complex system of embedded devices using local servers or taking advantage of advanced cloud technology, the OpenDOF Project can provide the solutions you need to enhance nearly any product, from the simplest resource-constrained devices to the most powerful computer networks.


